
The major intracellular cation is potassium. The extracellular fluid refers to all human body fluids apart from the intracellular compartment fluid and separates in three subdivisions: the blood plasma, the interstitial fluid and the transcellular fluid. Fluid compartments in an average 70-kg man. The extracellular compratment accounts for 14 L, the rest 1/3 of the total body weight. Since each membrane bound compartment has different function between one another, the concentration and the composition of the intracellular fluid is also different and heterogeneous even within one cell.Įxtracellular compartment Total body water is distributed between two major body fluid compartments: intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF) (Fig.

Intracellular Fluid (ICF) - fluid found in the cells (cytoplasm, nucleoplasm) comprises 60 of all body fluids. For example all the membranous organelles including the nucleus which surrounded by the phospholipid bilayer also contains fluid. Fluid Balance- The amount of water gained each day equals the amount lost Electrolyte Balance - The ions gained each day equals the ions lost Acid-Base Balance - Hydrogen ion (H +) gain is offset by their loss. ii) The plasma, which makes up almost one-fourth of the extracellular fluid, or about 3 liters.

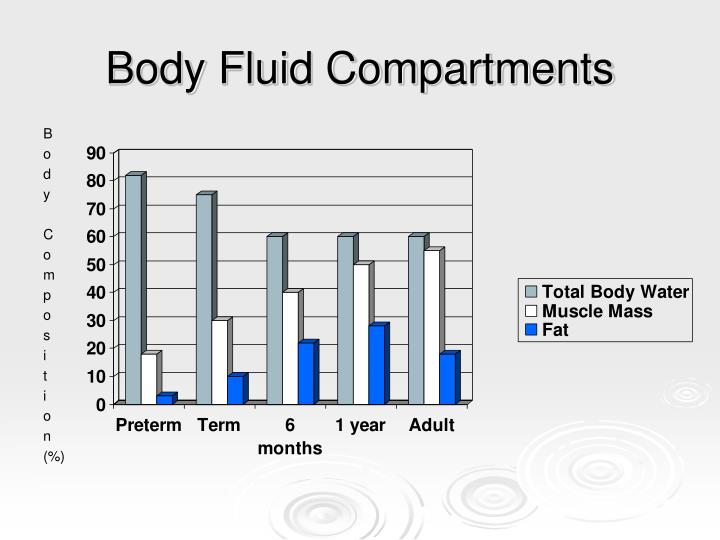
What are the two extracellular fluid compartments of the body The two main fluid compartments are divided by the cell membrane into the extracellular. These are the (1) intracellular fluid compartment, (2) interstitial fluid, and (3) plasma. The two largest compartments of the extracellular fluid are: i) Interstitial fluid, which makes up more than three-fourths (11 liters) of the extracellular fluid. In the human body plan, there are three major fluid compartments that are functionally interconnected. Besides cytosol however, there is also a small amount of fluid inside the cell that is not bound within the plasma membrane but rather by the organelle membrane. Total body water can be subdivided into two major compartments, intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF). It accounts for about 20 of the body weight, or about 14 liters in a 70-kg man. Materials travel between cells and the plasma in capillaries through the IF. Blood plasma is the second part of the ECF. The interstitial fluid (IF) is part of the extracellular fluid (ECF) between the cells. The intracellular fluid refers primarily to the fluid that is bound within the cellular plasma membrane called the cytosol. The intracellular fluid (ICF) is the fluid within cells. The intracellular compartment accounts for 28 L, the 2/3 of the total body weight. These pumps transport ions against their concentration gradients to maintain the cytosol fluid composition of the ions.Cytosol, the major constituent of the intracellular compartment shown at number 11 The reason for these specific sodium and potassium ion concentrations are Na+/K ATPase pumps that facilitate the active transport of these ions. Extracellular Fluids ECFs are similar except for the high protein content of plasma Sodium (Na +) is the major cation Chloride (Cl-)is the major anion Intracellular Fluids. In contrast to extracellular fluid, cytosol has a high concentration of potassium ions and a low concentration of sodium ions. Each fluid compartment of the body has a distinctive pattern of electrolytes. The cytosol also contains much higher amounts of charged macromolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, than the outside of the cell. The concentrations of the other ions in cytosol or intracellular fluid are quite different from those in extracellular fluid. The extracellular fluid, which is about 20 of total body weight can be subdivided into 2 sub-compartments: Plasma or intravascular fluid (20) and. The cell membrane separates cytosol from extracellular fluid, but can pass through the membrane via specialized channels and pumps during passive and active transport. The pH of the intracellular fluid is 7.4. The ECS is divided into three additional. Most of the cytosol is water, which makes up about 70% of the total volume of a typical cell. The human body is divided into two main compartments: intracellular space (ICS) and extracellular space (ECS).

These enzymes are involved in the biochemical processes that sustain cells and activate or deactivate toxins. fluid compartment: fluid inside all cells of the body constitutes a compartment system that is largely segregated from other systems. This mixture of small molecules is extraordinarily complex, as the variety of enzymes that are involved in cellular metabolism is immense. The cytosol or intracellular fluid consists mostly of water, dissolved ions, small molecules, and large, water-soluble molecules (such as proteins).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
